Electricity Rates
Electricity Rates
Electricity prices generally reflect the cost to operate the electricity grid, as well as the demand on the grid. Many factors play into electricity rates including:
- Fuel costs — This factor is cyclical in its nature. High electricity demand can increase demand for fuel (such as natural gas), which can result in higher prices for the fuel and eventually higher costs to generate the needed electricity.
- Power plants — Each plant has construction, maintenance, and operating costs.
- Electricity transmission and distribution systems — These systems have routine maintenance costs. Additionally, there can be incidental costs in the case of accidents or extreme weather.
- Weather conditions — Extreme temperatures increase the demand for electricity.
- Regulations — Some states have utility commissions that regulate prices, whereas others have a combination of regulated and unregulated prices.
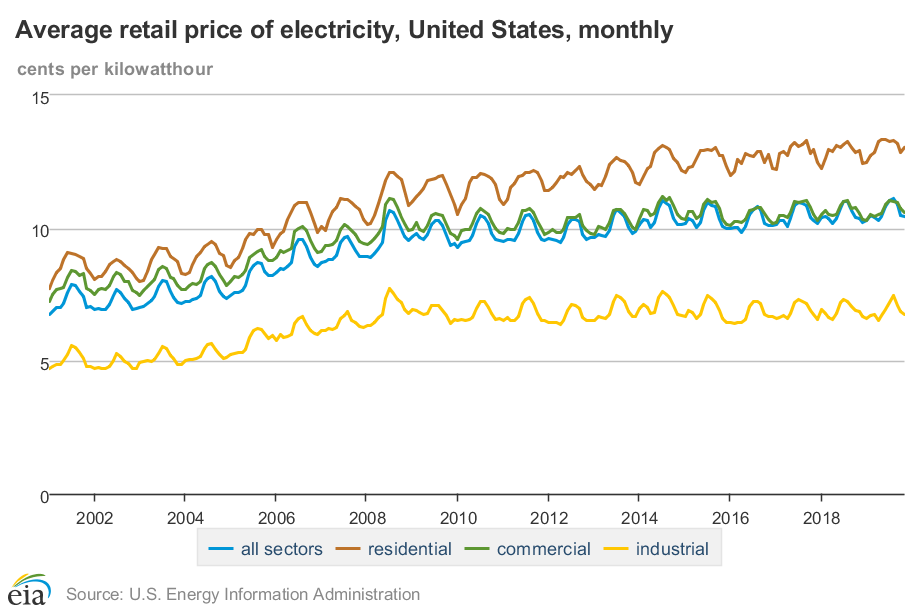
Thus, predicting the future cost of energy can be a major financial challenge in the global market and an unpredictable expense for businesses. As of 2019, the average electricity rate for commercial customers across the United States was 10.57 cents per kWh, according to the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA). However there are numerous rate and peak-demand structures that can have a tremendous impact on pricing from state to state. This fluctuating price structure is one of many reasons why facility owners are turning to solar power. Solar electricity allows companies to mitigate the risk of fluctuating electricity pricing by locking in a fixed rate for the term of a Power Purchase Agreement (PPA) contract or by directly participating in Net Metering by producing on-site power.
Regional Assessment
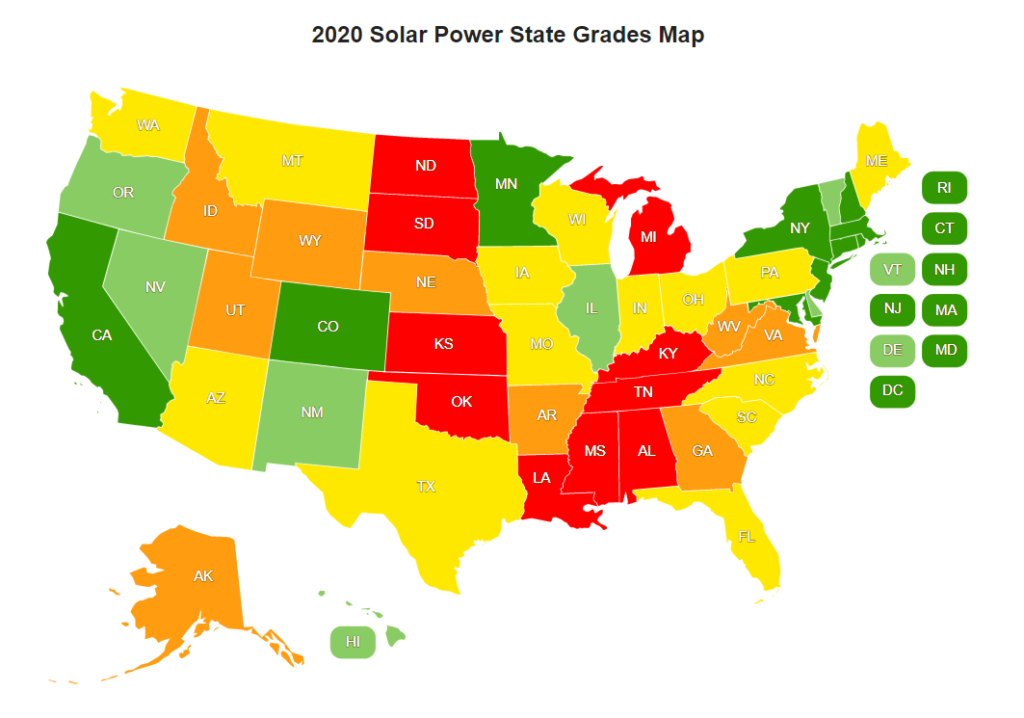
Electricity costs, tax credits, utility providers, and net metering regulations vary by region in the U.S. These are all important factors to consider when deciding if solar is right for your business. For information about your state, here is a great resource to monitor the latest solar rankings and information. And Melink Solar can help guide you through the decision process. To help navigate the regional viability of solar projects in the U.S., Melink Solar has assembled a high-level matrix of states based on a combination of solar irradiance and cost of energy. We have worked with customers across the country, managing different projects per regional codes and regulations.
Case Studies
No posts found.
